Polarization indicating the vectorial nature of light, has very important applications in the fields of optical communication, sensing, imaging and quantum optics. Recently, researchers from Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin University, Guilin University of Electronic Technology, The University of Texas at Austin, and The City University of New York successfully achieved full polarization manipulation under coherent control based on the bound states in the continuum(BIC) in the terahertz band using a simple silicon photonic crystal slab. The results were published in Nature Communications in August 2022 under the title "Coherent full polarization control based on bound states in the continuum".
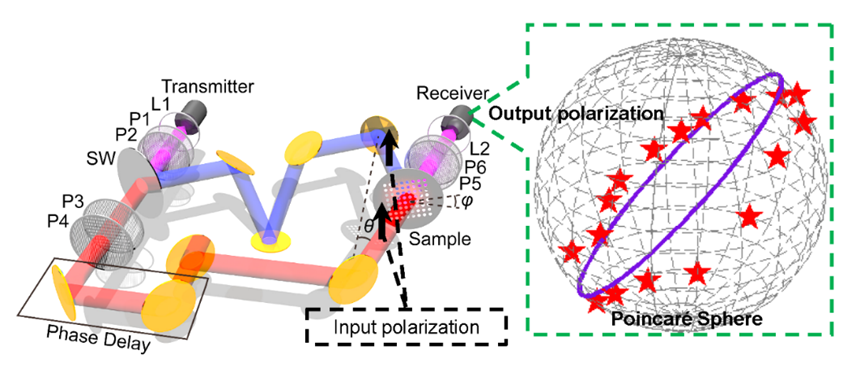
In this work, researchers extended the concept of coherent perfect absorbers to the polarization conversion. Combined with the polarization topology and incident angle sensitivity of the symmetry protected BICs in a silicon photonic crystal slab, efficient and real-time control of the output polarization state has been achieved in the terahertz band by finely controlling the relative phase delay of two input polarized waves. Through coherent control, the output polarization state can possibly cover the entire Poincare sphere by changing the incident angle and in-plane rotation angle of the silicon photonic crystal slab. The coherent control approach proposed in this article not only greatly expands the polarization control range of the symmetry protected BICs under single polarized light incidence, but also achieves real-time polarization state control, which provides new ideas for the research of active optical polarization control devices in different bands.
Prof. Kang Ming of Tianjin Normal University and Zhang Ziying of Tianjin University are the co-first authors of this article. Prof. Zhang Xueqian, and Prof. Han Jiaguang of Tianjin University, Dr. Alex Krasnok and Prof. Andrea Alù of the City University of New York are the corresponding authors of this article. Prof. Xu Quan and Wu Tong of Tianjin University have also made important contributions to this work. This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos.62025504, 61735012, 62075158, 61875150, 61935015, and 11974259).